What is Virtual PC? Understanding the Technology and its Benefits


Sharma bal
Table of content
- 1. Understanding What is Virtual PC Technology
- 2. Key Features of Virtual PC Software
- 3. Practical applications of Virtual PC
- 4. Common issues in Virtual PC usage
Ever wondered how you can run different operating systems on a single computer? Or test software in a safe, isolated environment? The answer lies in what is virtual pc technology. This guide will explore the fundamental concepts behind virtual PCs, their benefits, and why they’ve become an essential tool in modern computing.
1. Understanding What is Virtual PC Technology
At its core, a virtual PC, also known as a virtual machine (VM), is a software-based emulation of a physical computer. What is a virtual PC in practical terms? It’s like having a computer within your computer. Special software, called a hypervisor or virtualization software, allows you to abstract your computer’s hardware resources—such as the CPU, RAM, storage, and network adapter—and allocate portions of these resources to create one or more isolated virtual environments.
Think of it like this: your physical computer is the host, and the virtual PCs you create are the guests. Each guest virtual PC can run its operating system (like Windows, Linux, or macOS) and applications independently, just as if it were a separate physical machine. Statistically, the adoption of virtualization technology has seen a significant rise, with over 75% of enterprises utilizing virtualization in some form to improve resource utilization and flexibility.
Technical Point: The hypervisor acts as the manager, ensuring each virtual PC gets the resources it needs without interfering with other virtual PCs or the host operating system. There are two main types of hypervisors:
- Type 1 (Bare-metal): These hypervisors run directly on the host’s hardware (e.g., VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V Server).
- Type 2 (Hosted): These hypervisors run as an application on top of an existing operating system (e.g., VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, Parallels Desktop). They are more common for personal use.
Optimizing virtual PC lets you truly unlock the peak performance potential of it.
1.1. The Importance and Benefits of Virtualization: Why Use a Virtual PC?
Understanding what is virtual pc also means recognizing its profound impact on modern computing. Virtualization offers many benefits, making it crucial for individuals, developers, and businesses alike.
- Cost Reduction: By running multiple virtual PCs on a single physical machine, organizations can significantly reduce hardware costs, energy consumption, and cooling expenses. Studies have shown that server virtualization can save up to 60% in IT infrastructure costs.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability: Virtual PCs can be easily created, cloned, and moved between physical servers, providing unparalleled flexibility and allowing for rapid scaling of computing resources based on demand.
- Improved Disaster Recovery: VMs can be easily backed up and restored, making disaster recovery processes faster and more efficient. Snapshots of VMs allow for quick rollback to a previous state in case of system failures.
- Increased Efficiency and Resource Utilization: Virtualization optimizes hardware resources, ensuring that processing power, memory, and storage are utilized effectively, reducing wasted capacity.
- Simplified Management: Virtual PC software provides centralized management consoles, simplifying administrative tasks and reducing the complexity of managing multiple operating systems and applications.
- Safe Testing and Development Environments: Virtual PCs offer isolated environments for testing new software, configurations, or even potentially risky operations without affecting the host system. This is invaluable for developers and IT professionals.
Practical Hint: Use virtual PCs to test software compatibility across different operating systems before deploying it to a production environment. This can save significant time and prevent potential issues.
Running Incompatible Software: One key benefit of understanding virtual PCs is the ability to run older software or applications designed for a different operating system on your current computer. For example, you can run Windows-only applications on a MacOS machine or vice versa.
1.2 Popular Virtual PC Software Options
To experience the benefits of what is virtual pc technology, you’ll need virtualization software. Here are some popular options:
- VMware Workstation (Paid): A robust platform with advanced features, ideal for professionals, offering advanced features such as support for multiple operating systems, snapshotting, cloning, and network configuration.
- Oracle VirtualBox (Free): A cost-effective and widely used option suitable for personal use and testing.
- Target Audience: Oracle VirtualBox is suitable for developers, hobbyists, and users looking for a cost-effective virtualization solution for personal use or testing purposes.
- Practical Point: VirtualBox is open-source and has a large community, making it easy to find support and resources.
- Microsoft Hyper-V (Included in Windows Pro/Enterprise): A powerful option integrated directly into Windows, excellent for Windows-centric environments, offering features such as support for Windows and Linux guest operating systems, live migration, and integration with other Microsoft products and services.
- Technical Point: Hyper-V offers features like live migration and integration with other Microsoft services.
- Parallels Desktop (Paid, for macOS): Specifically designed for Mac users to run Windows and other OSes seamlessly, allowing them to run Windows and other operating systems alongside macOS. It offers features such as seamless integration with macOS, support for DirectX and OpenGL for gaming and graphics-intensive applications, and optimization for Apple M1 processors.
- Practical Hint: Parallels Desktop focuses on ease of use and integration with the macOS environment.
1.3. Comparing Virtual PC Software Options
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key features of these virtual PC software options:
| Feature | VMware Workstation | Oracle VirtualBox | Microsoft Hyper-V | Parallels Desktop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Paid | Free | Included in Windows | Paid |
| Guest OS Support | Windows, Linux, macOS | Windows, Linux, macOS | Windows, Linux | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Advanced Features | Yes | Limited | Yes | Yes |
| Integration | High | Moderate | High | High (with macOS) |
| Performance | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| User Interface | Advanced | Basic | Intermediate | Advanced |
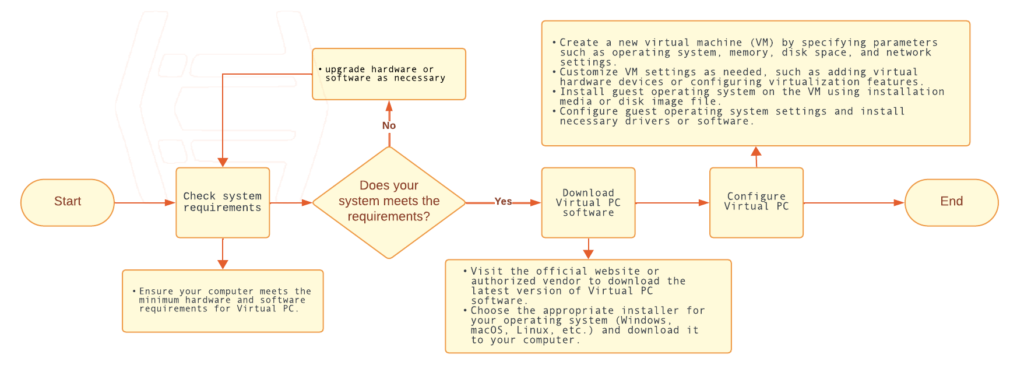
1.4 Installation and setup procedures for Virtual PC software on your computer.
2. Key Features of Virtual PC Software
Virtual PC software offers a range of key features that enhance the virtualization experience. Some common features include:
- Virtual Machine Creation: Users can create multiple virtual machines (VMs) within the software, each running its own operating system.
- Snapshotting: Allows users to capture the current state of a VM, enabling easy rollback to a previous state if needed.
- Cloning: Enables the duplication of existing VMs, saving time and effort in setting up new virtual environments.
- Networking Settings: Provides options for configuring network connections within VMs, including virtual switches and network adapters.
- Hardware Configuration: Allows users to adjust virtual hardware settings such as CPU, memory, and storage allocations for optimal performance.
- Practical Hint: Allocate only the necessary resources to your virtual PC. Over-allocating can impact the performance of your host system. Monitor resource usage within the VM to fine-tune allocations.
- Integration Tools: Facilitates seamless integration between host and guest operating systems, enabling features like file sharing and clipboard sharing.
- Remote Management: Allows users to manage virtual machines remotely, enhancing flexibility and convenience in virtualization management.
- Compatibility: Supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, ensuring flexibility in virtual environment setups.
These key features empower users to create, manage, and optimize virtualized environments to meet their specific needs and requirements.
3. Practical applications of Virtual PC
Virtualization offers numerous practical applications for software testing, development, and experimentation, including:
- Testing Compatibility: Developers can use virtualization to test software compatibility across multiple operating systems and environments without the need for physical hardware.
- Environments Isolation: Virtualization allows developers to isolate test environments, ensuring that changes or updates to one environment do not affect others.
- Snapshotting and Rollback: Developers can take snapshots of virtual machines at various stages of development, enabling quick rollback to a previous state if issues arise during testing.
- Reproducible Testing Environments: Virtualization enables developers to create reproducible testing environments, ensuring consistent testing results across different machines.
- Scalability Testing: Virtualization allows developers to easily scale up or down the resources allocated to test environments, enabling performance testing under various conditions.
- Automation Testing: Virtualization platforms often support automation tools, allowing developers to automate the testing process for improved efficiency and accuracy.
- Rapid Provisioning: Virtualization enables rapid provisioning of test environments, reducing the time required to set up and configure testing infrastructure.
- Parallel Testing: Developers can run multiple tests concurrently on virtual machines, speeding up the testing process and increasing overall productivity.
By leveraging virtualization for software testing, development, and experimentation, developers can improve the quality, reliability, and efficiency of their software development lifecycle. If you need any further help through your virtualization process, feel free to reach us at the Hostomize support group.
4. Common issues encountered by beginners in Virtual PC usage
| Common Issues | Troubleshooting Methods |
|---|---|
| Difficulty installing Virtual PC software | 1. Ensure system meets minimum requirements 2. Verify compatibility with host operating system 3. Examine the conflicting drivers or software 4. Re-download or obtain updated installation files 5. Seek online forums or support for specific installation troubleshooting guides |
| Performance degradation or sluggishness | 1. Allocate additional resources to virtual machines 2. Optimize host system performance (e.g., disk cleanup, memory management) 3. Check for resource-intensive applications running in background 4. Update Virtual PC software to latest version 5. Consider upgrading host hardware if necessary |
| Network connectivity issues | 1. Verify network adapter settings within virtual machines 2. Ensure proper network configuration (e.g., DHCP, static IP addressing) 3. Check firewall settings on host and guest operating systems 4. Restart networking services within virtual machines 5. Troubleshoot DNS or gateway issues |
| USB device not recognized in virtual machine | 1. Install Virtual PC extensions or guest additions 2. Enable USB support in virtual machine settings 3. Ensure proper USB device connection to host system 4. Check for driver compatibility with guest operating system 5. Reconnect USB device and restart virtual machine |